Papillomas on the body are a common condition in dermatological practice.The main sites are the armpits, neck, groin and genitals and face.Most tumors have a benign course, but the risk of transforming into skin cancer or cancer in any other local location increases under the influence of many negative factors.
Why are papillomas dangerous on the human body?

Viral tumors in the body are often caused by strains that have a fairly low carcinogenic risk and a minimal risk of cell degeneration.With atypical cells, rapid growth and changes in the structural features of papillary lesions are observed.
Today, particularly dangerous HPV strains include HPV types 15, 16, 18, 35, 51-59, 66-68.Interestingly, the location of the cancerous tumor during human papillomavirus infection can be absolutely any location.
Papillomas on the body appear as warts, calluses, flat or genital warts.The dangers and complications caused by HPV are often different between men and women.
Complications of papillomavirus in men
Often, men become carriers of infectious diseases and transmit them to women through unprotected sex.The main locations of papillomas on the body in men are the genitals, genitalia, frenulum and foreskin;Papillomas often form in the anus in men.Sometimes there are growths in the armpits and on the neck.
Symptoms directly depend on the location.The more typical clinical manifestation is the localization of papillomas in the genitals.Usually, tumors do not come with obvious symptoms.
The main complications in men are:
- prostate cancer;
- cancer of the nasopharynx and larynx;
- sexual impotence;
- infertility;
- erectile dysfunction;
- development of adenocarcinoma;
- Malignant tumors of the intestine.
The transformation of healthy cells into cancer cells is facilitated by:
- bad habits,
- difficult working conditions,
- frequent stress,
- permanent injury to papillary lesions;
- not hygienic enough.
Dangerous characteristics in women
In the absence of adequate treatment, HPV in women has a greater risk of causing complications due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the genital organs and hormonal levels.
The main complications are:
- cervical and adnexal cancer;
- dysplasia of the vulva, vaginal vault, cervical canal;
- uterine structural carcinoma;
- large genital warts, if papillomas are diagnosed in the groin in women;
- malignant changes in the mucous membrane of the pharynx, genital organs;
- Genital warts according to Lewandowski-Lutz pathological type;
- esophageal and laryngeal cancer;
- plant cancer.
The localization of warts and warts in the lumen of the urethral canal leads to interruption of urine outflow.When localized in the larynx - hoarseness and impaired respiratory function.
Unfortunately, many women notice any new growth on their skin solely from the perspective of a cosmetic issue.By removing the papilloma, they hope to have completely solved the HPV problem.When the viral infection is active, the removed tumors reappear and with greater intensity.
It is important to promptly recognize signs of tumor malignancy:
- Changes in shape, size and structure of growth;
- Instability of the ampulla of papillary lesions:
- Pain in the growth area;
- Continuous trauma, bleeding, infection.
Frequent exposure to negative factors contributes to the destabilization of growth and stimulates cell change into cancerous cells.
If papillomas appear, a dermatologist should be consulted to clarify the nature of the pathological rash.
Are papillomas on the body contagious?
Are papillomas on the body transmitted from person to person?Considering the high transmissibility of human papillomavirus infection, patients wonder about the possibility of acquiring the virus through contact with viral tumor foci on the skin.The answer is clear - it is almost impossible to “catch” the virus when touching the papilloma.
However, if the skin of the carrier and healthy person in the contact area is damaged, the risk of infection increases.
There are many other ways the disease is transmitted:
- sexual intercourse;
- labor activities;
- household contact route (long time living with virus carrier).
You can also become infected in public places, especially in bathhouses, saunas, locker rooms and swimming pools.
There is the concept of self-infection, when a damaged papilloma causes many other papillomas on the entire body surface.
The entry of a virus into the human body does not mean that a rash on the skin will necessarily appear after some time.With the high immune response of the human body, the amount of antibodies is enough to block the activity of viruses of any strain, and on the basis of good health, the virus does not appear at all until the end of life.
Of course, even if a person has no symptoms, he or she is still a carrier of the virus.
Many papillomas appear on the body, what does this mean?
The appearance of papillomas on the body in many different locations characterizes the activation of viral strains.Multiple foci of papillomas signal an increased risk of malignant growth.The increase in pathogenic activity of viral strains is due to decreased immunity with persistent progression.
The following may reduce the body's immune response:
- colds;
- hypothermia;
- stress factors;
- alcohol and drug addiction;
- persistent hormonal disorders;
- pregnancy, abortion;
- Chronic pathology of internal organs.
Viral activity can be triggered simply by non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.On the physical side, multiple papillomas explain pathologies of organs and internal systems.HPV is often associated with other viral diseases, such as herpes infection.
Papillomas have spread throughout the body - what to do?
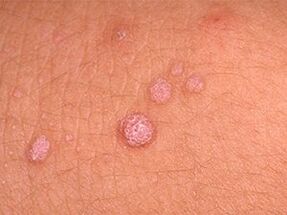
When multiple papillomas appear, it is important to undergo differential diagnosis.A professional doctor usually immediately notes the nature of the rash and points out the possible cause of the lump.
The main research methods are:
- blood test for anti-viral antibodies;
- Digen test to determine the type of strain, virus structure and risk level of causing cancer;
- Polymerase chain reaction to detect viral DNA;
- Cytological examination of biological material from the cervical canal;
- histological examination of samples from female genital organs;
- analysis of warts or warts.
A preliminary diagnosis is usually made during the patient's first examination.Based on the results of the study and the patient's clinical history, viral infection is diagnosed or ruled out.It is important to separate HPV from dermatological diseases, cancers, and herpes viruses.
Fights papillomas on the body
Today there is no effective therapy against viral infections, but official medicine can facilitate a stable remission of the disease and prevent skin rashes.Infection itself is not dangerous, but papilloma formation increases the risk of cellular malignancy and tumor appearance.
Treatment
One promising direction is drug treatment:
- Interferon-based immunomodulators to stimulate the immune system;
- Antiviral drugs;
- Vitamins create strong immunity and restore the body;
- Local preparations for removing papillomas.
In case of secondary infection, bacteriotherapy and antiseptic treatment are prescribed.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable for pain relief.
Remove
It is possible to remove the tumor using modern hardware techniques and plastic surgery.
There are several effective methods for removing the tumor:
- lancet;
- laser;
- radio waves;
- cold destruction;
- chemicals;
- electric condenser.
No activity prevents the formation of further pathological tumors.Without adequate antiviral treatment, eliminating external signs brings only temporary results.
HPV is a common infection that can be transmitted through sexual contact, as well as through frequent kissing.The main prevention is to vaccinate children aged 12-14 before their first sexual intercourse.It is important to monitor skin and genital hygiene.Unfortunately, even barrier methods of contraception cannot guarantee 100% protection from human papillomavirus infection.A patient's prompt response to the rash is key to safe and prompt treatment, including preventing the risk of cancerous tumors.

























